Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 p diodes by MeV range heavy ions
p diodes by MeV range heavy ionsOshima, Takeshi; Iwamoto, Naoya; Onoda, Shinobu; Wagner, G.*; Ito, Hisayoshi; Kawano, Katsuyasu*
Surface & Coatings Technology, 206(5), p.864 - 868, 2011/11
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:18.97(Materials Science, Coatings & Films)Charge induced in n p Silicon Carbide (6H-SiC) diodes by heavy ions, oxygen (O), silicon (Si), nickel (Ni), and gold (Au) using a Transient Ion Beam Induced Current (TIBIC) measurement system. The slight increase in collected charge shows in a low bias region, and then, the values are saturated in a high bias region. This indicates that in the low bias region, since the length of the depletion layer is shorter than the ion range, carriers induced in deeper than the depletion layer diffuse and annihilate before they reach the depletion layer. Since the length of the depletion layer increases with increasing bias voltage, the charge collected by diodes increases with increasing bias voltage. In the case of the high bias, the length of the depletion layer is longer than the ion range. As a result, all carriers are induced in the depletion layer, and they can be collected by the electric field. Thus, This indicates that the value of collected charge does not depend on bias voltage. From the point of view of charge collection efficiency (CCE), the collected charge decrease with increasing atomic number. From the calculation, it is found that dense electron-hole pairs were generated in SiC by irradiation of ions with heavy mass. The decrease in the CCE due to ion irradiation with heavy mass can be interpreted in terms of the annihilation of e-h pairs in plasma due to the Auger recombination.
p Silicon Carbide (6H-SiC) diodes by heavy ions, oxygen (O), silicon (Si), nickel (Ni), and gold (Au) using a Transient Ion Beam Induced Current (TIBIC) measurement system. The slight increase in collected charge shows in a low bias region, and then, the values are saturated in a high bias region. This indicates that in the low bias region, since the length of the depletion layer is shorter than the ion range, carriers induced in deeper than the depletion layer diffuse and annihilate before they reach the depletion layer. Since the length of the depletion layer increases with increasing bias voltage, the charge collected by diodes increases with increasing bias voltage. In the case of the high bias, the length of the depletion layer is longer than the ion range. As a result, all carriers are induced in the depletion layer, and they can be collected by the electric field. Thus, This indicates that the value of collected charge does not depend on bias voltage. From the point of view of charge collection efficiency (CCE), the collected charge decrease with increasing atomic number. From the calculation, it is found that dense electron-hole pairs were generated in SiC by irradiation of ions with heavy mass. The decrease in the CCE due to ion irradiation with heavy mass can be interpreted in terms of the annihilation of e-h pairs in plasma due to the Auger recombination.
Abe, Hiroshi; Aone, Shigeo*; Morimoto, Ryo*; Uchida, Hirohisa*; Oshima, Takeshi
Transactions of the Materials Research Society of Japan, 36(1), p.133 - 135, 2011/03
The introduction of vacancies in Pd was found to be effective for an increase in the initial hydrogen absorption rate in a previous study. Also, it was reported that the initial hydrogen absorption rate depends strongly on the surface conditions of metals. Heavy ions with keV ranges can create severe damage and high densities of vacancy near the surface of materials. As well known, the formation of hydride phases can be facilitated by the presence of vacancy because vacancy acts as hydrogen trapping site to form hydrides. Thus, the hydrogen absorption characteristics of Pd may be improved by the irradiation of heavy ions. As a result, the initial hydrogen absorption rate increased due to ion irradiation, and the value became 3 10 times higher than un-irradiated Pd.
10 times higher than un-irradiated Pd.
Shiine, Yasuharu*; Nishikawa, Hiroyuki*; Furuta, Yusuke*; Sato, Takahiro; Ishii, Yasuyuki; Kamiya, Tomihiro; Nakao, Ryota*; Uchida, Satoshi*
no journal, ,
Onuki, Shun*; Abe, Hiroshi; Matsumura, Yoshihito*; Uchida, Hirohisa*
no journal, ,
Hydrogen storage alloys are required high hydrogen absorption rate for the negative electrodes of the Ni-MH batteries applications. Surface modifications are crucial to improve the reactivity of hydrogen with metals because the dissociation of the H molecules in the gas phase or the dissociation of the H
molecules in the gas phase or the dissociation of the H O molecules in an electrochemical process is the first step of the overall reaction of hydrogen absorption by metals. In the present study, irradiation effects on electron beam and charged ions on hydriding characteristics of LaNi
O molecules in an electrochemical process is the first step of the overall reaction of hydrogen absorption by metals. In the present study, irradiation effects on electron beam and charged ions on hydriding characteristics of LaNi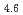 Al
Al alloy were studied. The hydrogen absorption rare measurements were also performed for the irradiated and un-irradiated samples using an electrochemical method. The crystal structure and phase of the bulk of the irradiated alloys were determined by X-ray diffraction. We will discus the effects of irradiation fo electron beam and ions on the improvement of the rate of hydrogen absorption by the LaNi
alloy were studied. The hydrogen absorption rare measurements were also performed for the irradiated and un-irradiated samples using an electrochemical method. The crystal structure and phase of the bulk of the irradiated alloys were determined by X-ray diffraction. We will discus the effects of irradiation fo electron beam and ions on the improvement of the rate of hydrogen absorption by the LaNi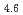 Al
Al alloys.
alloys.
Umenyi, A. V.*; Hommi, Masashi*; Miura, Kenta*; Hanaizumi, Osamu*; Yamamoto, Shunya; Inoue, Aichi; Yoshikawa, Masahito
no journal, ,
Various works on silicon (Si)-based luminescent materials utilizing the quantum confinement effect, such as Si nanocrystals (Si-NC's), have been reported. Typical fabrication methods of Si-NC's are co-sputtering of Si and SiO , Si-ion implantation into SiO
, Si-ion implantation into SiO plates, and so on. In this work, we observed ultraviolet (UV)-light emission from Si-ion-implanted fused-silica substrates under different implanting conditions. The implantation energy was 80 keV, and the implantation amount was 2
plates, and so on. In this work, we observed ultraviolet (UV)-light emission from Si-ion-implanted fused-silica substrates under different implanting conditions. The implantation energy was 80 keV, and the implantation amount was 2 10
10 ions/cm
ions/cm . The Si-implanted substrates were annealed at 1100
. The Si-implanted substrates were annealed at 1100 1250
1250 C. Photoluminescence (PL) spectra were measured with excitation using a He-Cd laser. UV-PL spectra having peaks around a wavelength of 370 nm were observed from all the samples. The UV-peak wavelengths of the samples are almost the same in spite of the various annealing temperatures. Si-ion-implanted fused-silica are expected to be useful as light sources for next-generation optical-disk systems.
C. Photoluminescence (PL) spectra were measured with excitation using a He-Cd laser. UV-PL spectra having peaks around a wavelength of 370 nm were observed from all the samples. The UV-peak wavelengths of the samples are almost the same in spite of the various annealing temperatures. Si-ion-implanted fused-silica are expected to be useful as light sources for next-generation optical-disk systems.
Koshikawa, Hiroshi; Usui, Hiroaki*; Maekawa, Yasunari
no journal, ,
Hybrid membranes consisting of polyimide (PI) films embedded with copper wires were prepared by electroplating copper into the etched pores of ion track membranes. Electrical resistance of single copper wire, measured by the four-point probe, did not show significant difference with the value estimated from the bulk resistivity. It was also found that the resistance, as well as the hybrid membrane structure, remains stable against thermal treatment of at least up to 400 C. Such anisotropically conducting membranes with high thermal stability are expected to have wide application in microelectronics devices.
C. Such anisotropically conducting membranes with high thermal stability are expected to have wide application in microelectronics devices.